Access Specifiers in C++
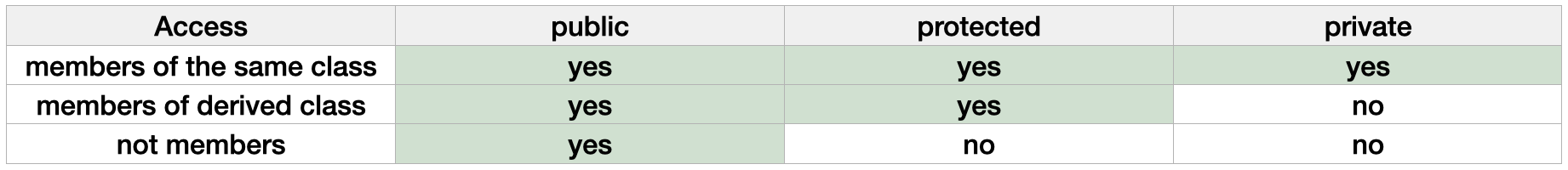
Access specifiers in C++ determine the accessibility of the class members. There are three types:
- Public members: accessible from anywhere where the object is visible.
- Protected members: accessible from other members of the same class (or from their "friends"), but also from members of their derived classes.
- Private members: accessible only from within other members of the same class (or from their "friends").
Code Example
Below is an example that illustrates the usage of access specifiers:
Explanation
- BaseClass has three members with different access specifiers:
- public_member: accessible from anywhere.
- protected_member: accessible within BaseClass and DerivedChass.
- private_member: only accessible within BaseClass.
- DerivedChass inherits from BaseClass:
- dispProtected(): Can access protected_member because it's inherited.
- Trying to access private_member directly will fail because it's private to BaseClass.
- In the main function:
- We create an object derivedObj of DerivedChass.
- Access the public_member directly.
- Call dispProtected() to access protected_member.
- Call dispPrivate() to access private_member through a public member function of BaseClass.
Conclusion
Access specifiers are crucial in C++ for encapsulating data and controlling access to class members. They help in maintaining the integrity of data and providing secure access mechanisms.