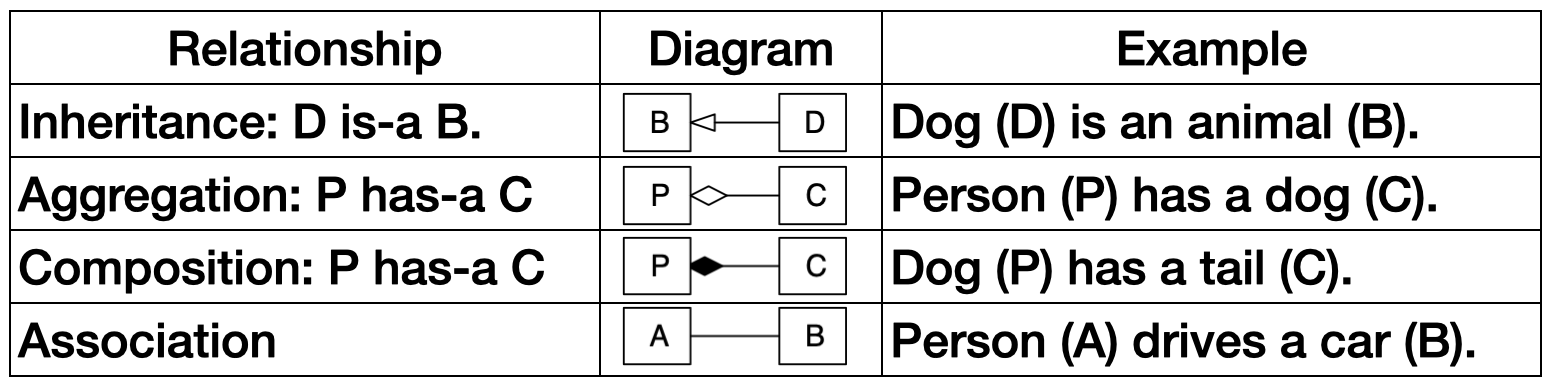
C++ class relationship
- Inheritance: "is-a" relationship. It allows a class (derived class) to inherit attributes and methods from another class (base class).
- Composition: "has-a" relationship. It means that one class contains objects of another class as its members. If the containing object is destroyed, the contained objects are also destroyed.
- Aggregation: "has-a" relationship but with weaker bonds compared to composition. The lifetime of the contained objects does not depend on the lifetime of the container.
- Association: a more general relationship between classes, where objects of one class interact with objects of another class without any ownership or containment.
Code Example
Below is an example illustrating these relationships:
Explanation
- Inheritance: Dog inherits from Animal. This means Dog is an Animal and can access its methods and attributes (if any were defined in Animal).
- Composition: Dog contains a Tail object. When a Dog object is destroyed, the Tail object is also destroyed.
- Aggregation: Person has a pointer to a Dog object (p_dog). The Dog object exists independently of the Person object and can be shared among different Person objects.
- Association: Person has a method drive which takes a Car object as an argument. Person and Car are loosely related, meaning they interact without ownership or containment.
Conclusion
Understanding class relationships helps in designing robust and maintainable object-oriented programs. These relationships define how objects of different classes interact and how the lifecycle of one object may affect another.